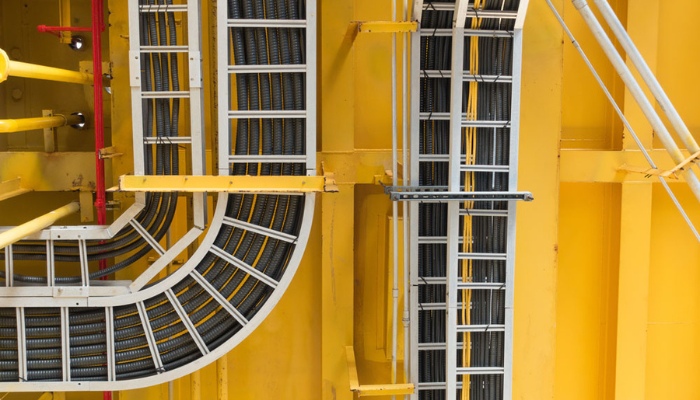
We all know that cable trenches are used for laying power cables, and weld the load-bearing angle steel frame on the side wall of the trench and ground it according to the design requirements and covered with a cover plate. Its purpose is to lay cables underground as a dedicated passage. The cable tray is a reserved channel for laying cables and wires inside of a building, which is a shaft set up for various lines, through which these cables are sent to various households.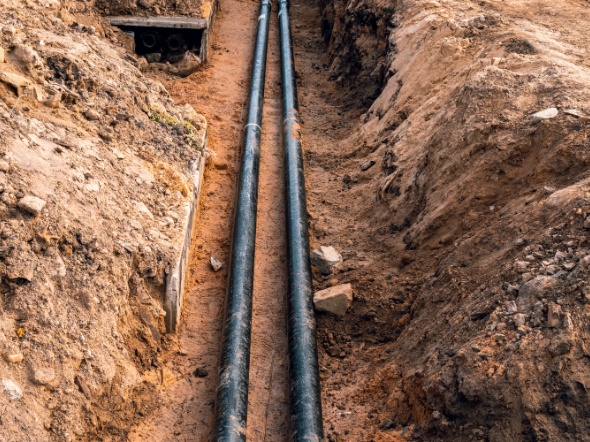 
General regulations for power cable installation:
1. power cables should be protected from mechanical external forces, overheating, corrosion, and other hazards; Under the condition of meeting safety requirements, the shortest cable path should be ensured; It should be easy to lay and maintain; It is advisable to avoid areas where excavation and construction will be carried out.
2.The power cable should meet the allowable bending radius requirements for any laying method and all changes in its path conditions.
3. When there are several cables in the same channel, like control cable, instrumentation cable, fiber optical cable, ethernet data cable etc if laid on multiple supports on the same side, the following regulations should be met:
① It should be arranged in order of voltage level from high to low power cables, strong to weak control and signal cables, and communication cables from top to bottom;
② When the number of support layers is limited by channel space, adjacent voltage level power cables of 35kV and below can be arranged on the same support layer, and power cables of 1kV and below can also be configured on the same support layer as strong current control cable and signal cables;
③ When the working and backup cables of the same important circuit are separated by fire resistance, they should be configured on brackets on different layers
4> Exposed cables should not be laid parallel to the upper part of the heating pipeline. Allowable distance between cables and pipelines without barrier protection.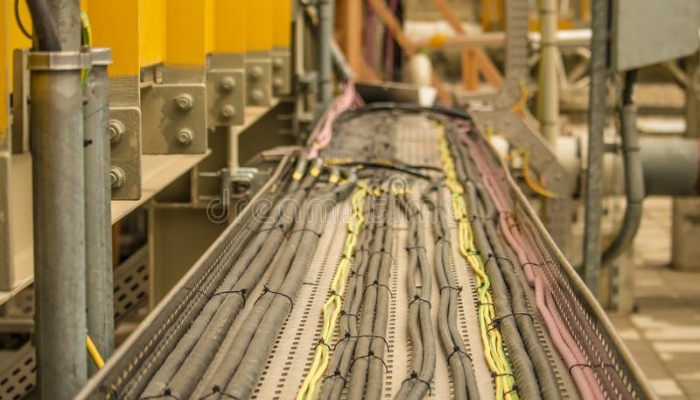
Selection of power cable laying method :
1.The selection of cable laying method should be based on factors such as engineering conditions, environmental characteristics, cable type and quantity, as well as the principles of reliable operation, easy maintenance, and reasonable technology and economy.
2. The selection of cable direct burial laying method should comply with the following regulations:
① For 35kV and below power cables with less than 6 cables in the same path, direct burial should be used in areas where frequent excavation is not easy to occur, such as remote auxiliary facilities or suburban areas in the factory area; Direct burial can also be used in situations where it is easier to renovate under urban sidewalks or at road edges.
② In areas with a large number of underground pipeline networks within the factory area, there may be areas where molten metal or high-temperature liquids spill out, areas with frequent excavation for development, or soil areas corroded by chemical or stray currents, direct burial should not be used.
3> Selection of cable conduit laying method:
① Exposed cables laid in explosive hazardous areas, exposed cables that need to be protected on the ground, and when underground cables intersect with highways or railways;
② Underground power cables pass through sections of houses and squares, as well as sections where cables will be laid as roads in the planning;
③ When there are a large number of cables in factory areas with dense underground pipeline networks, narrow urban roads with heavy traffic or difficult road excavation channels;
4> When using shallow groove laying method:
① Places with high groundwater levels.
② The number of power cables in the channel is relatively small, and it is located in outdoor distribution devices and other places where there are not often heavy trucks passing through. For control rooms, relay protection rooms, etc. with a large number of cables, it is advisable to set up cable interlayer at the bottom; When the number of cables is small, a cable layer with a movable cover plate can also be used. In places with high groundwater levels and areas where chemical corrosive liquids overflow, support type overhead laying should be used in the factory building. When underground laying is not suitable for buildings or factory areas, overhead laying can be used.
5> Underground direct burial laying:
Currently, most of the external cables in our project are directly buried and should comply with the following regulations:
① The cable should be laid in the trench and a soft soil or sand layer with a thickness of not less than 100mm should be laid on the upper and lower adjacent sides along the entire length of the cable.
② A protective plate with a width not less than 50mm on both sides of the cable should be covered along the entire length of the cable, and the protective plate should be made of concrete.
③ When directly burying urban cables, it is advisable to lay eye-catching signs on the upper layer of the protective board.
④ Located in suburban or open areas, clear directional signs or stakes should be erected at straight intervals of 100m along the cable path, at turns or joints.
⑤ When cables are laid in trenches through corrugated pipes, plain concrete with a thickness of not less than 100mm should be poured along the entire length of the corrugated pipe, and the width should not be less than 50mm on the outer side of the pipe. The cable may not contain an armor layer.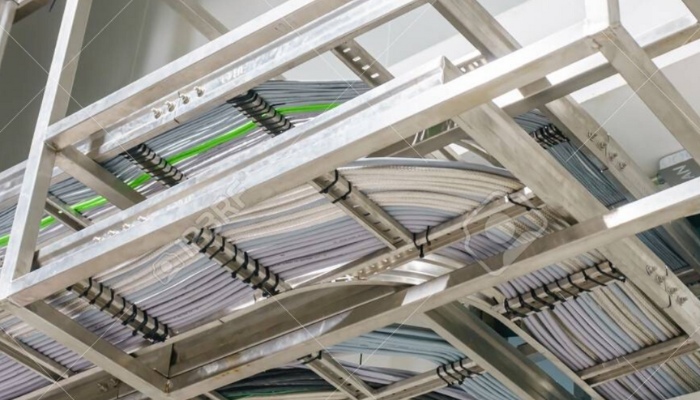
When directly buried in non frozen soil areas, the burial depth of cables should comply with the following regulations:
① The distance from the cable sheath to the foundation of underground structures shall not be less than 0.3m.
② The depth from the cable sheath to the ground should not be less than 0.7m;
③ When located in the traffic lane or underground, it should be deepened appropriately and should not be less than 1.0m. When directly buried in permafrost areas, it is advisable to bury it below the permafrost layer,
When deep burial is not possible, it can be buried in dry frozen soil layers or backfill soil with good soil drainage, and other measures can be taken to prevent cable damage.
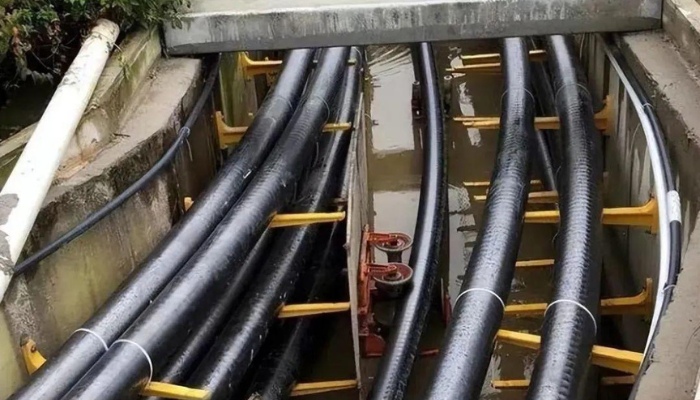

The selection of the diameter of the protective tube and the number of cables passing through should comply with the following regulations:
① Each cable conduit should only be threaded with one cable. Except for power plants, Electrical substation and other important places, for all circuits of a motor or all circuits of low-voltage motors of the same equipment, no more than 3 power cables or multiple control cables can be combined in each pipe.
② The inner diameter of the conduit should not be less than 1.5 times the outer diameter of the cable or the outer diameter of multiple cable envelopes. The inner diameter of the conduit hole for the exhaust pipe should not be less than 75mm.
When using exhaust conduits, the following regulations should be met:
① The number of conduit holes should be reserved appropriately for future use.
② power cables with significant differences in conductor operating temperatures should be configured in different tube banks with appropriate spacing.
③ The soil cover thickness on the top of the pipeline should not be less than 0.5m.
④ The pipeline should be placed on a leveled and compacted soil layer with sufficient cushion blocks to maintain continuity and straightness; The longitudinal drainage slope should not be less than 0.2%.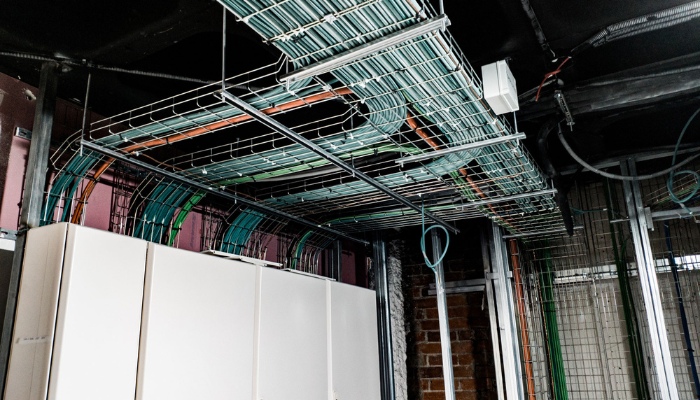
03 Relevant requirements for cable tray construction:
1> Cable trays should be installed at the following locations in longer cable pipelines:
① At the spacing of cable tension limit.
② At cable branches and joints.
③ Major changes in pipeline direction or cables transitioning from pipes to directly buried locations
④ Necessary reinforcement and fixing points for pipelines with large slopes and to prevent cable slippage.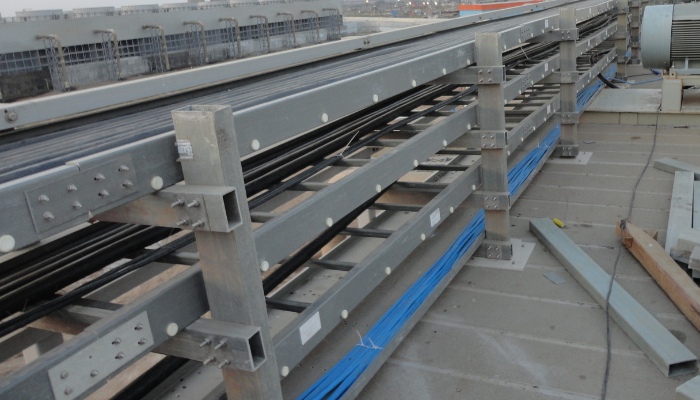
Construction requirements for cable trenches:
1> The cable trench in the distribution room is generally used for the incoming and outgoing lines of distribution equipment, and is basically divided into single and double cable trenches under the cabinet.
2> The cable trench wall is made of MU10 autoclaved lime sand bricks, constructed with M5 cement sand mortar, and the trench wall is plastered with 1:2 cement mortar. The top and foundation are all made of C20 concrete; Channel steel should be embedded below the equipment.
3> The clear width of the cable trench, tunnel, or working well passage should comply with relevant standards and requirements
4> The interlayer distance between cable supports, ladders, or trays should meet the requirements for convenient cable laying, fixation, and placement of joints. In the case of multiple cables placed on the same layer, any cable and its joint can be replaced or added; When using cable cross-section
When the outer diameter of the joint is not very large, the minimum distance between layers of cable supports, ladders, or trays that meet the above requirements can be taken from the values listed in the following table:
5> When laying horizontally, the layout dimensions of the top and bottom layers of the cable support should comply with the following regulations:
① The minimum allowable net distance between the top bracket and the top plate or beam bottom of the structure should meet the allowable bending radius requirements when connecting the cable bow to the upper cabinet panel, and should not be less than the sum of the numbers listed on the previous page plus 80~150mm.
② The clear distance between the top bracket and other equipment should not be less than 300mm; When unable to meet the requirements, protective boards should be set up.
③ The minimum distance between the lowest support and the bottom of the floor and trench must also meet certain requirements
PowerTel & his associated factories can provide you a wide of range of low, medium. high voltage power cable, and its cable tray & raceway, including a value engineering design for your whole electrical distribution system.
Please feel free to contact our expert engineers.
